Abstract
Case Report
Chlorambucil induced papilledema: a serious yet reversible side effect of chemotherapy
Sulena and Himanshu Kaushal*
Published: 25 April, 2022 | Volume 6 - Issue 1 | Pages: 013-014
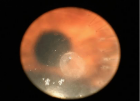
Papilledema is optic disc swelling due to high intracranial pressure. Possible conditions causing high intracranial pressure and papilledema include intracerebral mass lesions, cerebral hemorrhage, head trauma, meningitis, hydroce-phalus, spinal cord lesions, impairment of cerebral sinus drainage, anomalies of the cranium, and idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) [1].
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.ijceo.1001044 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
References
- Rigi M, Almarzouqi SJ, Morgan ML, Lee AG. Papilledema: epidemiology, etiology, and clinical management. Eye Brain. 2015; 7: 47-57. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28539794/
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. "PubChem Compound Summary for CID 2708, Chlorambucil" PubChem. 2021. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Chlorambucil
- Bregeat M, Hernians R. Oedenia papillaire spontanerrient criable aucous d'um traitement par le chlorambucil. Bull SOC Beige Oplztlialmol. 1972; 1960567-69.
- Al-Tweigeri T, Nabholtz JM, Mackey JR. Ocular toxicity and cancer chemotherapy: A review. Cancer. 1996; 78: 1359-1373. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8839540/
- Gonsalves WI, Zent CS, Pulido JS, Patnaik MM. Visual loss in early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31: e280-e282. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23650405/
Figures:
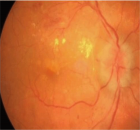
Figure 1
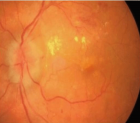
Figure 2
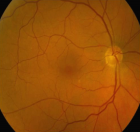
Figure 3
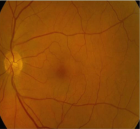
Figure 4
Similar Articles
-
A Comparative Study of Anatomic and Functional Outcomes of Two Surgical Techniques of Cataract at LomeAyena KD*,Santos KAM,Vonor K,Amedome KM,Wodome A,Strauss G,Nagbe YE,Koffi-Ametooyona A, Balo K. A Comparative Study of Anatomic and Functional Outcomes of Two Surgical Techniques of Cataract at Lome . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hceo.1001001; 1: 001-008
-
Theory and Experiments. (+) Add Reading Glasses to Prevent MyopiaPeter R Greene*,Brown OS. Theory and Experiments. (+) Add Reading Glasses to Prevent Myopia . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hceo.1001002; 1: 009-022
-
Efficacy of early Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Central Retinal Artery OcclusionAyse Gul Kocak Altintas*,Mehmet Citirik. Efficacy of early Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy in Central Retinal Artery Occlusion . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hceo.1001003; 1: 023-028
-
Mitomycin-C Use and Complications in OphthalmologyTongabay Cumurcu*. Mitomycin-C Use and Complications in Ophthalmology. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hceo.1001004; 1: 029-032
-
Intravitreal Ranibizumab/ Lucentis (IVTL) injections in Glaucoma patients-Intraocular Pressure (IOP) elevation and the use of Anterior Chamber Paracentesis (ACP)EA Ansari*. Intravitreal Ranibizumab/ Lucentis (IVTL) injections in Glaucoma patients-Intraocular Pressure (IOP) elevation and the use of Anterior Chamber Paracentesis (ACP) . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hceo.1001005; 1: 033-041
-
Detection of Ganglion Cell Loss in Preperimetric Glaucoma by Fourier-Domain Optical Coherence TomographySuneeta Dubey*, Baswati Prasanth,Lokesh Chauhan, Saptarshi Mukherjee. Detection of Ganglion Cell Loss in Preperimetric Glaucoma by Fourier-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hceo.1001006; 1: 042-048
-
Intravitreal ranibizumab in the management of acute central serous ChorioretinopathyIbrahim Nawaiseh,Ahmad Halawa*,Dina Alardah. Intravitreal ranibizumab in the management of acute central serous Chorioretinopathy . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.hceo.1001007; 1: 049-054
-
The Role of Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acids in Dry Eye DiseaseWilliam J Faulkner*. The Role of Omega-3 Essential Fatty Acids in Dry Eye Disease . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijceo.1001008; 1: 055-059
-
Neuro-ophthalmological emergency disorders: A general viewBurak Turgut*,Feyza Çaliş Karanfil, Fatoş Altun Turgut. Neuro-ophthalmological emergency disorders: A general view . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijceo.1001009; 1: 060-066
-
Prospective Clinical Study to Find out Epidemiology of Xerophthalmia in Children in a Tertiary Care Centre in IndiaDeepak Mishra*,Megha Gulati,Prashant Bhushan,Nilesh Mohan,Bibhuti Sinha P. Prospective Clinical Study to Find out Epidemiology of Xerophthalmia in Children in a Tertiary Care Centre in India . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.ijceo.1001010; 1: 066-070
Recently Viewed
-
Development of qualitative GC MS method for simultaneous identification of PM-CCM a modified illicit drugs preparation and its modern-day application in drug-facilitated crimesBhagat Singh*,Satish R Nailkar,Chetansen A Bhadkambekar,Suneel Prajapati,Sukhminder Kaur. Development of qualitative GC MS method for simultaneous identification of PM-CCM a modified illicit drugs preparation and its modern-day application in drug-facilitated crimes. J Forensic Sci Res. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001043; 7: 004-010
-
A Gateway to Metal Resistance: Bacterial Response to Heavy Metal Toxicity in the Biological EnvironmentLoai Aljerf*,Nuha AlMasri. A Gateway to Metal Resistance: Bacterial Response to Heavy Metal Toxicity in the Biological Environment. Ann Adv Chem. 2018: doi: 10.29328/journal.aac.1001012; 2: 032-044
-
Obesity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease as a Separate Clinical PhenotypeDaria A Prokonich*, Tatiana V Saprina, Ekaterina B Bukreeva. Obesity in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease as a Separate Clinical Phenotype. J Pulmonol Respir Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001060; 8: 053-055
-
Current Practices for Severe Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Associated COPD and EmphysemaMJ Nicholson*, M Seigo. Current Practices for Severe Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency Associated COPD and Emphysema. J Pulmonol Respir Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001058; 8: 044-047
-
Navigating Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Current and Emerging Therapies for Neurodegenerative DisordersShashikant Kharat*, Sanjana Mali*, Gayatri Korade, Rakhi Gaykar. Navigating Neurodegenerative Disorders: A Comprehensive Review of Current and Emerging Therapies for Neurodegenerative Disorders. J Neurosci Neurol Disord. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnnd.1001095; 8: 033-046
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."